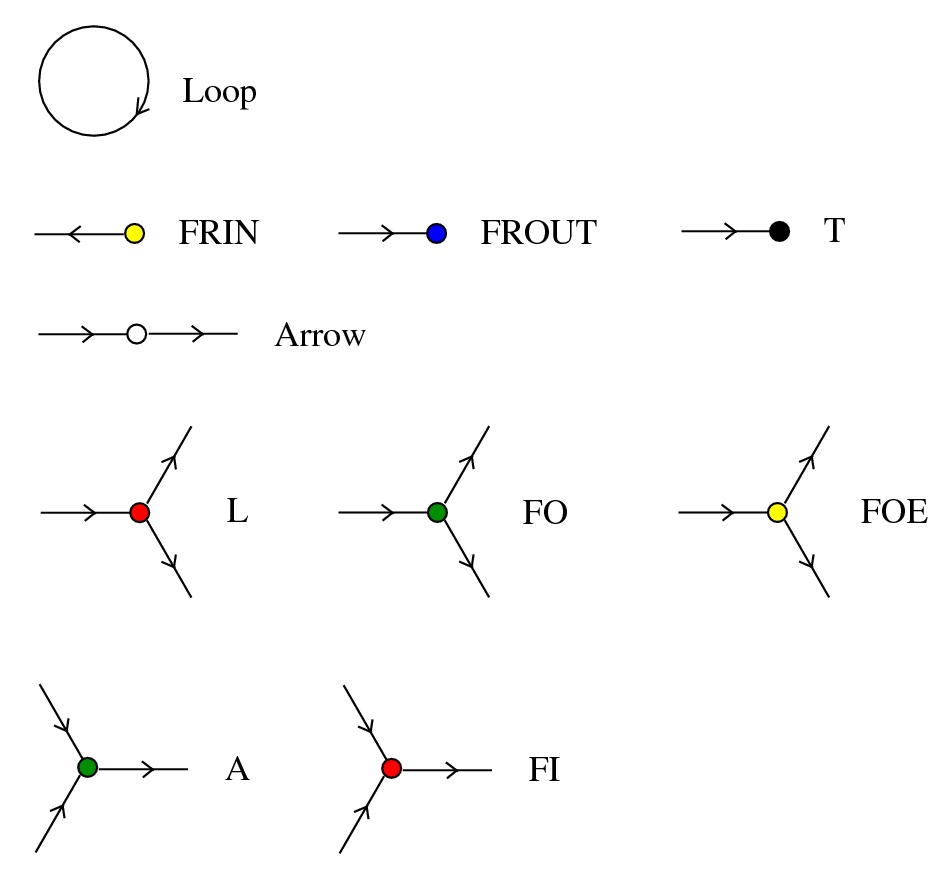
Artificial Physics for Artificial Chemistries
(1) artificial chemistries
(2) chemlambda
(3) information content of the deviation from hamiltonian evolution
(4) chemlambda + physics
[Dittrich, P., Ziegler, J.,
Banzhaf, W. (2001)] - an artificial chemistry is a triple (S,R,A):
S - a class of molecule types
R - a class of chemical reactions
A - an algorithm for the application of the chemical reactions to
a multiset of molecules
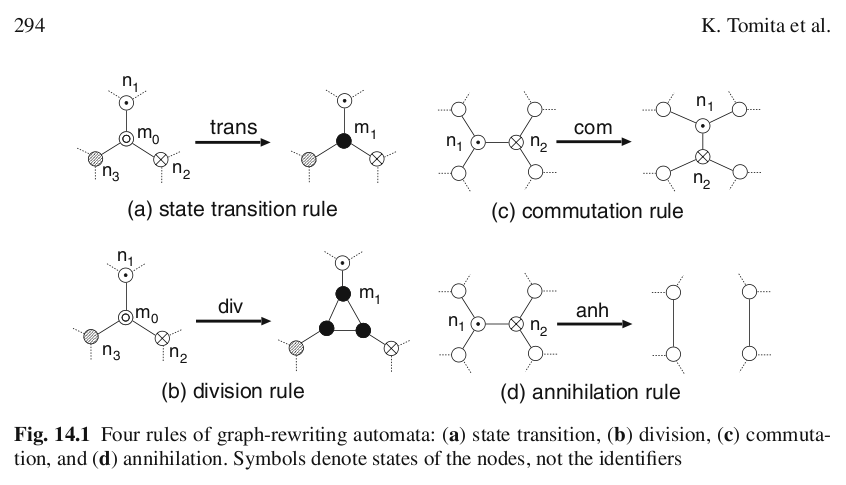
[K. Tomita, H. Kurokawa,
S. Murata (2009)] - a graph-rewrite automaton is a triple (S,R,A):
S - a class of graphs for example trivalent graphs with colored nodes
R - a class of graph-rewrites
A - an algorithm for the application of the
graph-rewrites to one graph
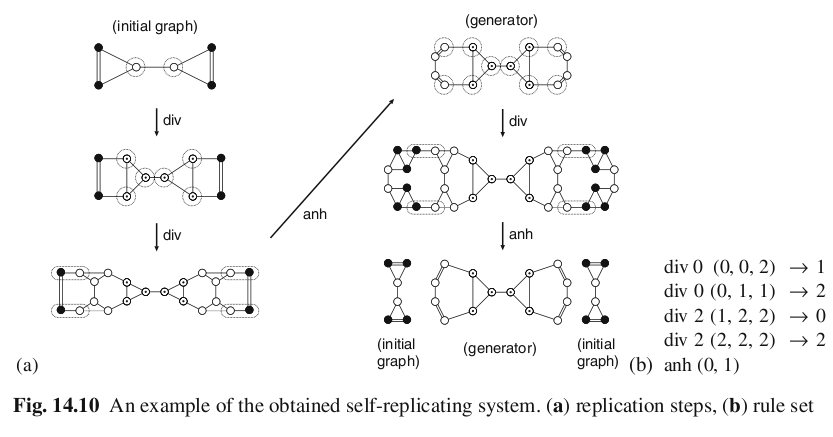
- an asynchronous graph-rewrite automaton is a triple (S,R,A):
S - a class of "molecules" (i.e. of graphs)
R - a class of "chemical reactions" (i.e. graph-rewrite rules)
A - a random and local algorithm for the application of
graph-rewrites to one graph

λ calculus [A.
Church (1936)] is a term rewrite system
Terms:
- variable: x, y, z, ...
- term:
- variable |
- A B where A, B terms |
- λx.A where x var, A term
Term rewrite rule:
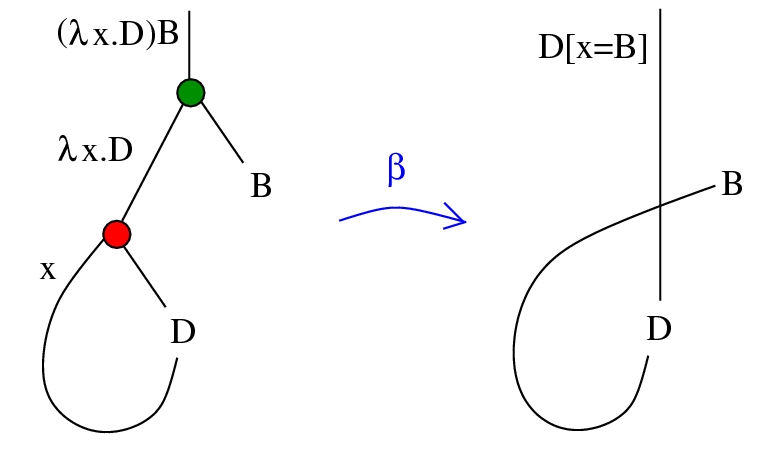
- β-reduction: (λx.A)B → A[x=B]
λ calculus [A.
Church (1936)] is a term rewrite system
Term rewrite rule:
- β-reduction: (λx.D)B → D[x=B]
(1971, C.P. Wadsworth, 1990, J. Lamping) graph rewrite system
[W. Fontana, L. W. Buss (1994)]
- ALCHEMY = ALgorithmic Chemistry:
S - a class of λ- terms in normal form
R - a class of reductions
A + B → A + B + normal form of AB
A - algorithm of random application of a reaction to a random selection of terms
[G. Berry,
G. Boudol (1992)]
- CHAM = Chemical Abstract Machine: a programming
language which uses molecules, solutions and transformation rules
[Y. Lafont (1997)]
Interaction combinators
S - a class of trivalent fatgraphs
R - a class of graph rewrite rules, without conflicts
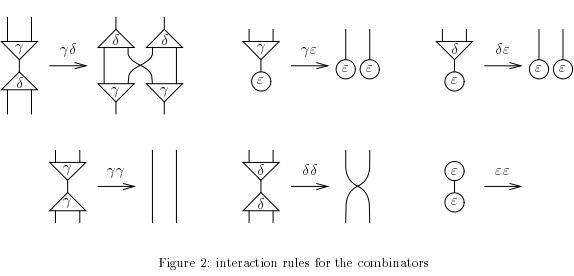

A - any algorithm will do for graphs which reduce in a finite number of steps
The Matrix: what does it mean?
"still he'd see the matrix in his sleep, bright lattices of logic unfolding across that colorless void" (William Gibson, Neuromancer)
"still he'd see the matrix in his sleep, bright lattices of logic unfolding across that colorless void" (William Gibson, Neuromancer)
versus
Blade Runner:
is this alive?


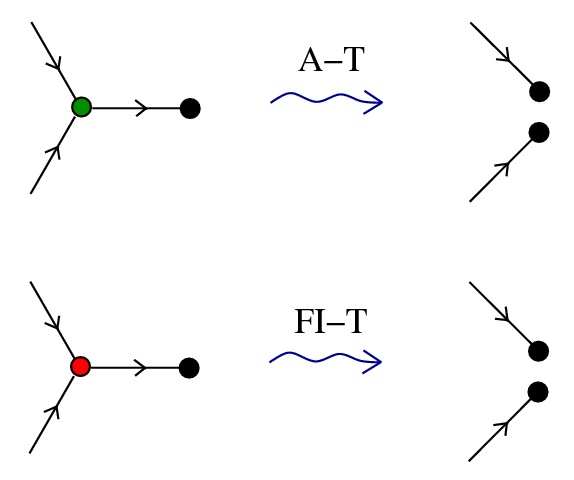
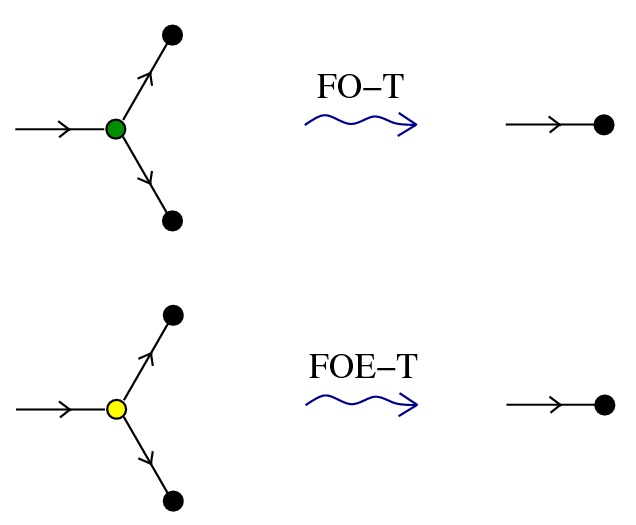
R - two main families of graph rewrite rules
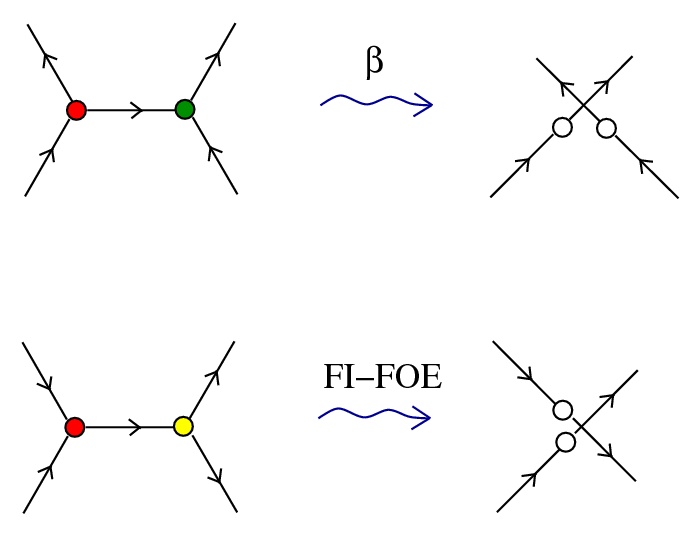
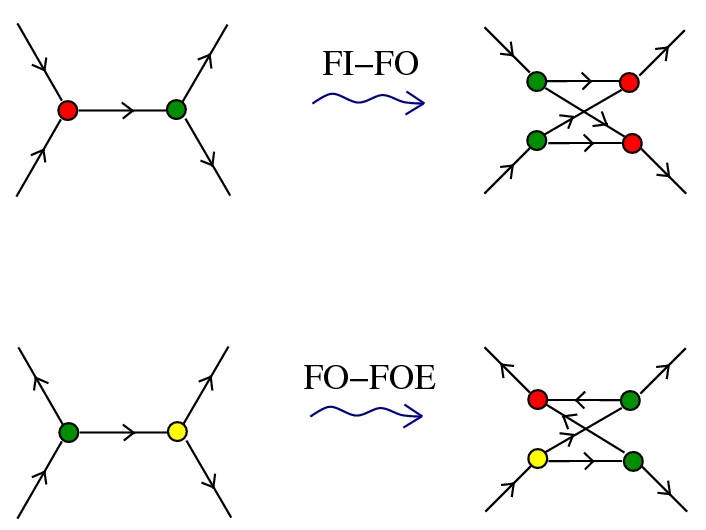
which look like the IC rewrites
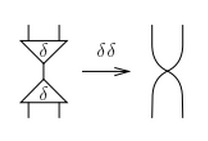
each IC node has only 1 active port, so no conflicts
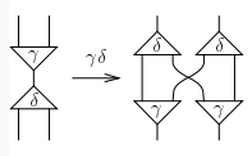
however chemlambda nodes have 2 active ports, leads to conflicts
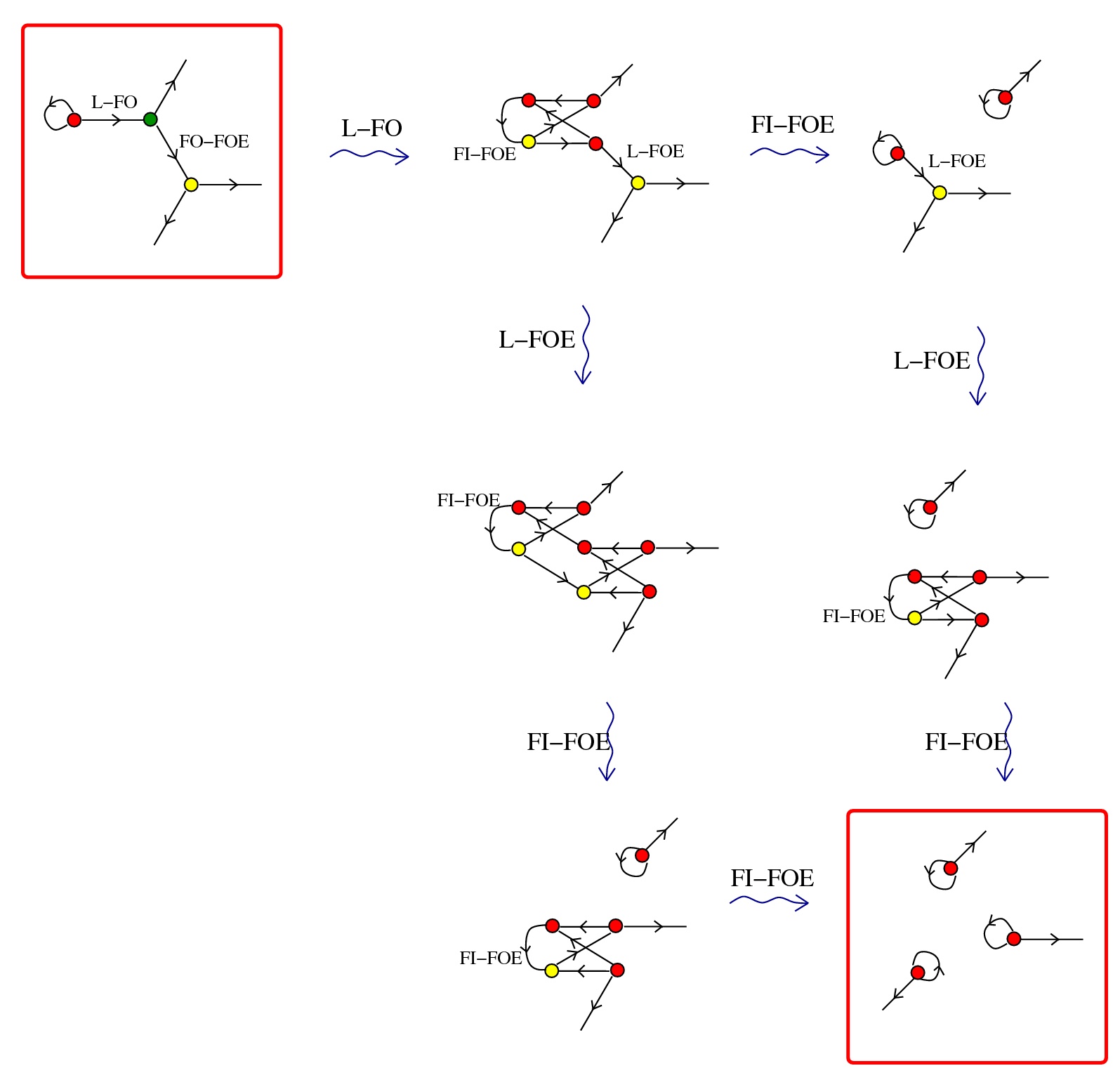
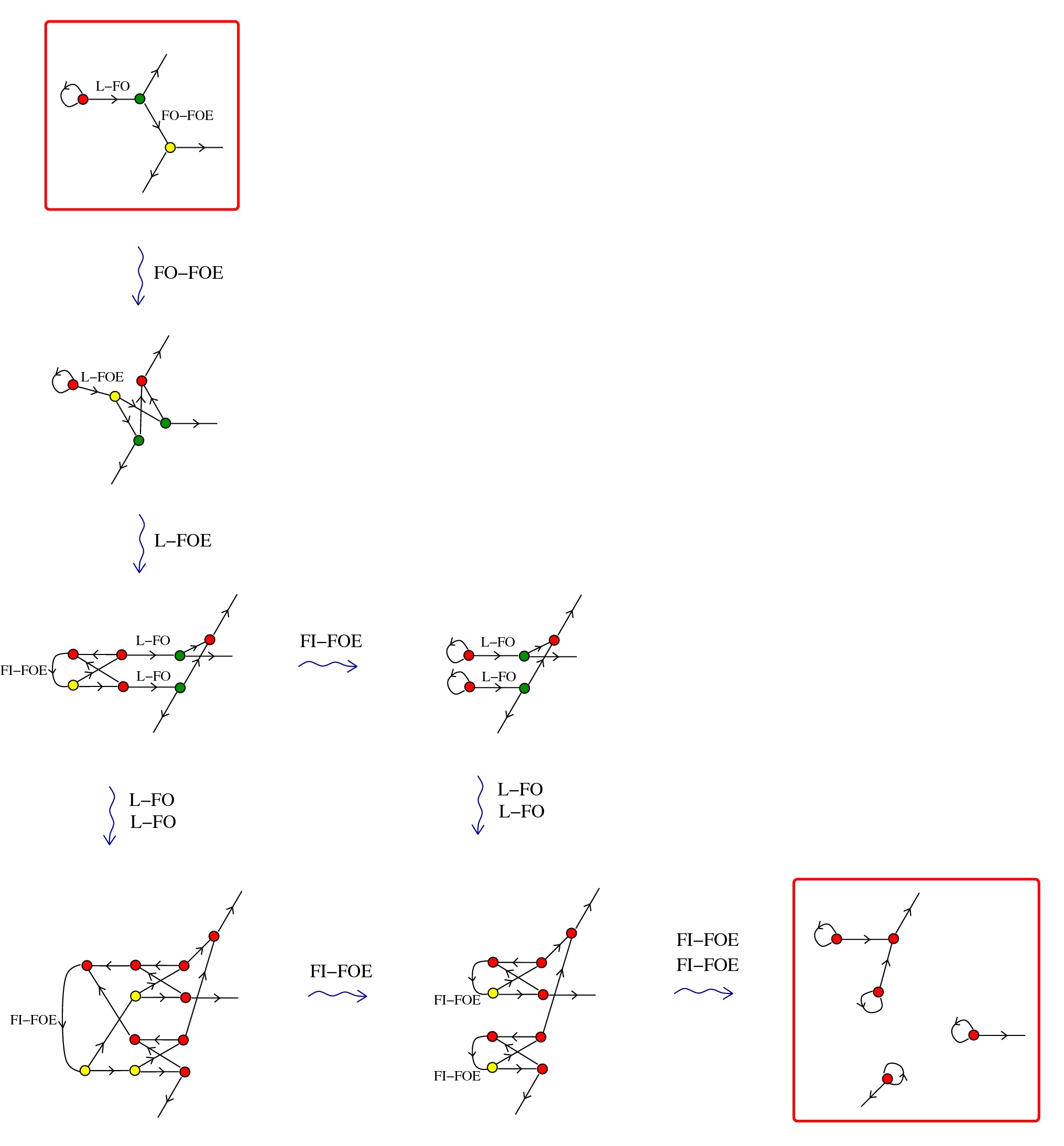
R - a COMB graph rewrite cycle to eliminate the Arrow elements and loops
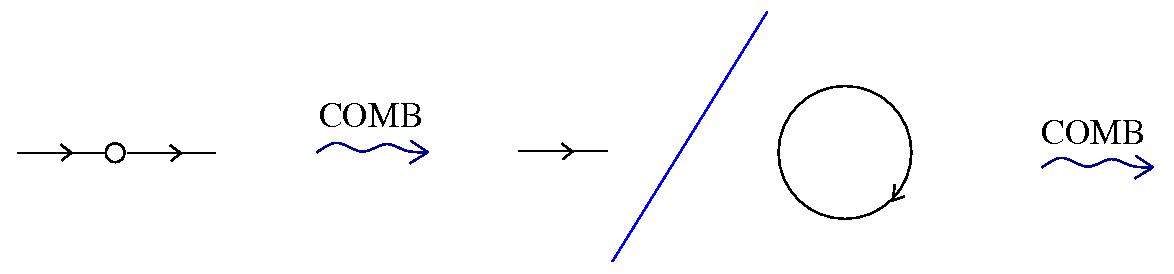

R - and some TERM rewrites like the other IC rewrites


Dodecahedron multiplication

Tube pattern duplication

Tube pattern with Turing Machines, builts itself

The factorial of 5: (a,b) to (a+1, ab)

Properties:
Turing universal: we can represent λ-terms and rewrites, or TM.
[Ackermann(2,2) simulation] [Demos] [Molecular computers (2015)] arXiv:1811.04960
[Ackermann(2,2) simulation] [Demos] [Molecular computers (2015)] arXiv:1811.04960
gives many interesting graphs modified outside λ-calculus




artificial life: a chemlambda quine is a graph deterministically periodic, evolving under the random algorithm.
[Library of molecules] [Collection of simulations]
[Library of molecules] [Collection of simulations]
The information content of the deviation from hamiltonian evolution, an extension of
Hamiltonian mechanics.
[Buliga (2009)]
[(2018)]
[(2019)]
[Buliga, de Saxce (2017)]
aka "Hamiltonian inclusions with convex dissipation" or
"symplectic Brezis-Ekeland-Nayroles principle"
define the deviation from hamiltonian evolution vector η
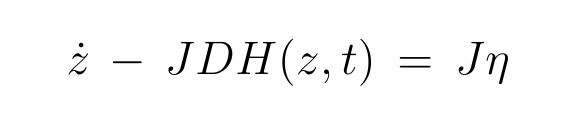
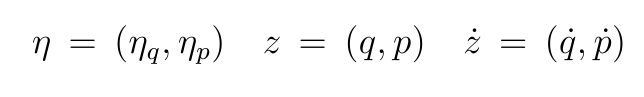
impose that the evolution minimizes the information content
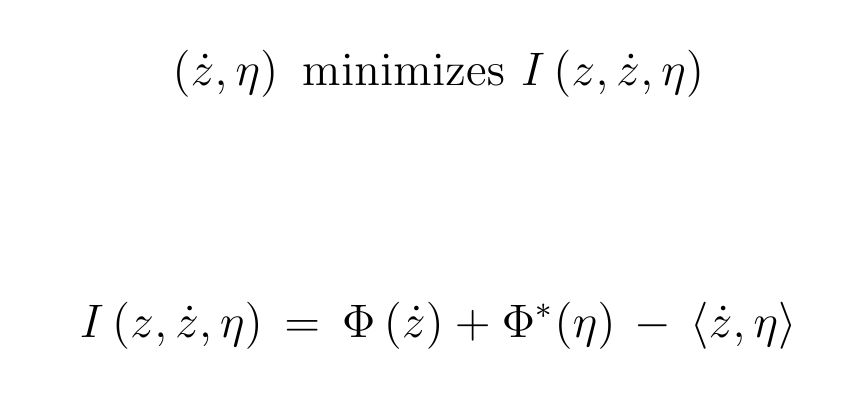
allows dissipation (a generalized Liouville theorem)

applies to: viscosity, plasticity, damage, fracture
also to unilateral contact (and friction)
[E. Fredkin, T. Toffoli (1982)]
billiard ball computer
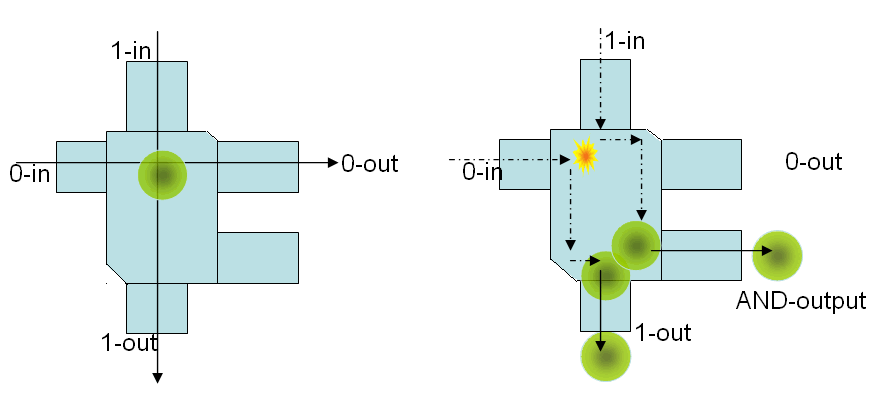
Let M be the space (billiard), then the information content function is
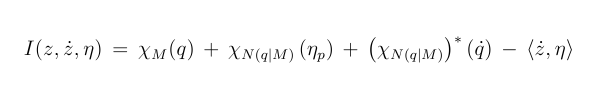
stochastic version
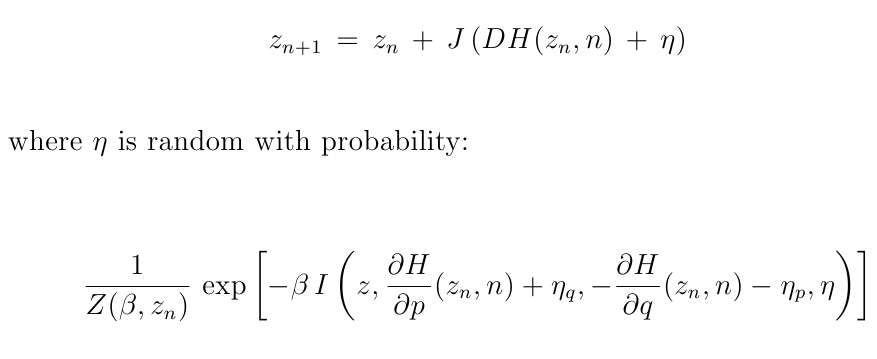
chemlambda+physics
A version of chemlambda
is a billiard ball computer (with the physics as in the principle of minimal information content),
with some of the state variables over a pair of
permutohedra
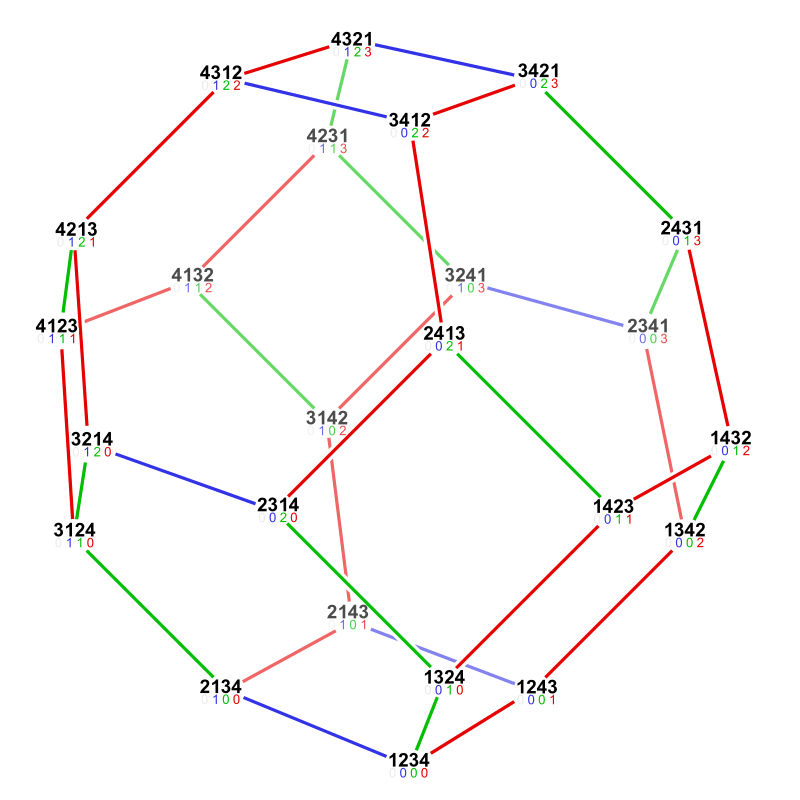
chemlambda+physics
anatomy of nodes and edges:
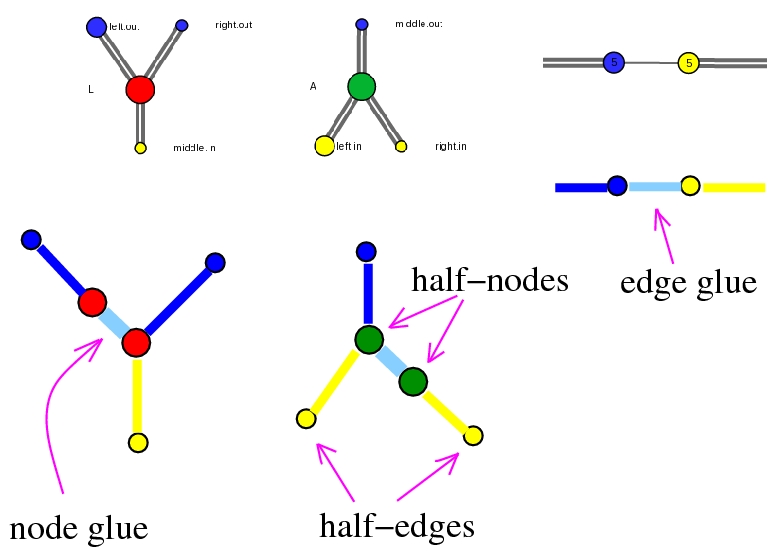
chemlambda+physics
initial graph:
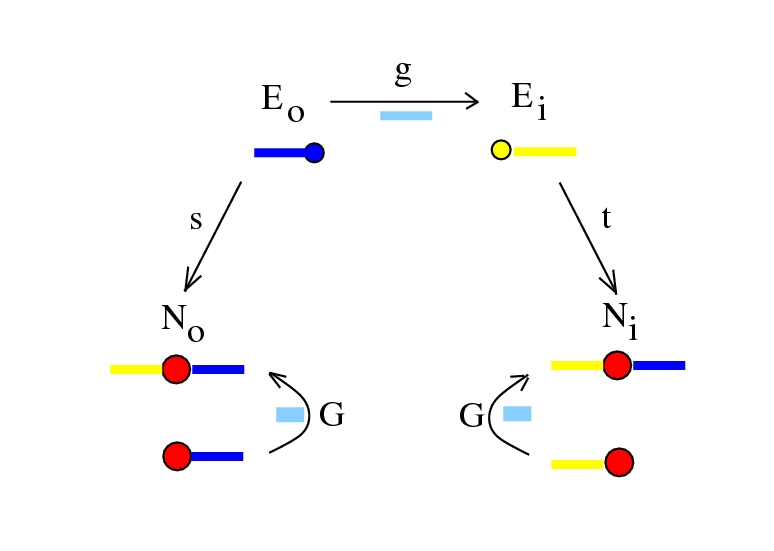
chemlambda+physics
a rewrite is a pair of permutations:
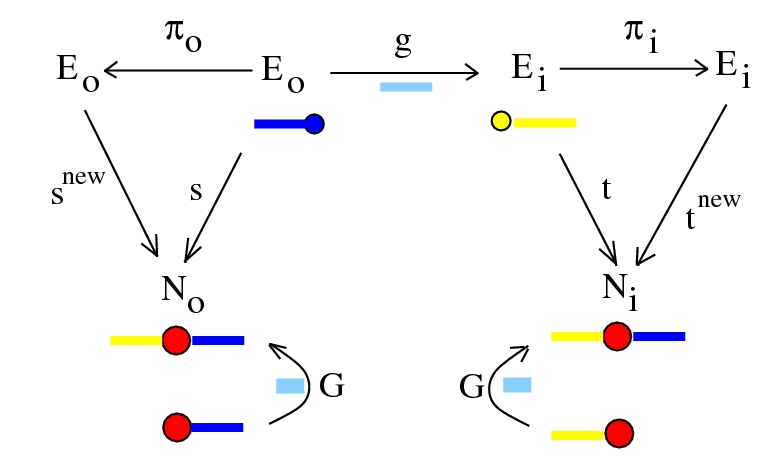
chemlambda+physics
we modify the hamiltonian of the force graph by using the state of the graph
we modify the information content and we use the stochastic version
... and it works (announcement).
CONCLUSION: is a game with a pair of permutohedron dices.
Continue to my homepage